Return-to-Workplace Mandates
After World Warfare II ended, the nation’s labor pressure returned to civilian life. By the tip of 1945 greater than 4 million troopers returned to civilian standing. Greater than six million girls held wartime jobs in factories and three million volunteered with the Crimson Cross. Authorities archives reporting on girls within the labor pressure throughout World Warfare II reported on the aftermath: “After the warfare, most girls returned house, let go from their jobs. Their jobs, once more, belonged to males. Nonetheless, there have been lasting results. Ladies had confirmed that they may do the job and inside a number of a long time, girls within the workforce turned a typical sight.”
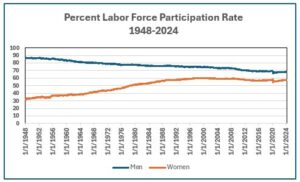
Firstly of 1948 the post-war sample of households with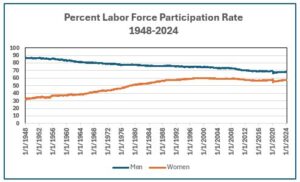 working fathers and homemaker moms was effectively established. The labor pressure participation price for males aged 16-64 was 87 p.c, and for ladies, 32 p.c. Because the chart illustrates, the 2 charges moved towards converging over the next seven a long time. By the beginning of 2020, the speed for males had fallen to 69 p.c, however the price for ladies elevated to 58 p.c. The Covid-19 pandemic of 2020 and its aftermath disrupted employment tendencies for each women and men.
working fathers and homemaker moms was effectively established. The labor pressure participation price for males aged 16-64 was 87 p.c, and for ladies, 32 p.c. Because the chart illustrates, the 2 charges moved towards converging over the next seven a long time. By the beginning of 2020, the speed for males had fallen to 69 p.c, however the price for ladies elevated to 58 p.c. The Covid-19 pandemic of 2020 and its aftermath disrupted employment tendencies for each women and men.
Between February and April of 2020 the USA misplaced over 22 million jobs. The primary months of job restoration noticed females returning at a slower tempo than males, however when the chance for distant work turned widespread, it’s credited with fueling a file price of feminine labor pressure participation. A research by the San Francisco Federal Reserve discovered that participation modified for various subsets of the feminine labor pressure: “…girls with out a school diploma disproportionately dropped out of the labor pressure throughout the pandemic, maybe to care for youngsters or sick kin. Nonetheless, we discover that ladies with a school diploma or extra more and more joined the labor pressure throughout this era, doubtlessly due to extra alternatives to earn a living from home.”
Now Return-to-Workplace (RTO) mandates are threatening to erase the positive aspects. Whereas a current survey by McKinsey discovered that 9 out of ten girls need to work remotely all or a part of the time, a worldwide survey discovered that just about two-thirds of CEOs count on staff to return to places of work 5 days per week by 2026.
The enchantment of distant working is shared by female and male employees alike, each part-time and full-time, in keeping with numerous surveys. Companies have contrasting views on the advantages of office-only work: whereas some see increased productiveness when folks earn a living from home, others stress some great benefits of in-person collaboration. Examples abound of employees planning to stop if given an RTO mandate, and of employees keen to just accept much less pay for a distant work alternative. All that is occurring in a demographic atmosphere of fewer births, an ageing inhabitants, and a smaller work pressure.
Return-to-Workplace Mandates
After World Warfare II ended, the nation’s labor pressure returned to civilian life. By the tip of 1945 greater than 4 million troopers returned to civilian standing. Greater than six million girls held wartime jobs in factories and three million volunteered with the Crimson Cross. Authorities archives reporting on girls within the labor pressure throughout World Warfare II reported on the aftermath: “After the warfare, most girls returned house, let go from their jobs. Their jobs, once more, belonged to males. Nonetheless, there have been lasting results. Ladies had confirmed that they may do the job and inside a number of a long time, girls within the workforce turned a typical sight.”
Firstly of 1948 the post-war sample of households with working fathers and homemaker moms was effectively established. The labor pressure participation price for males aged 16-64 was 87 p.c, and for ladies, 32 p.c. Because the chart illustrates, the 2 charges moved towards converging over the next seven a long time. By the beginning of 2020, the speed for males had fallen to 69 p.c, however the price for ladies elevated to 58 p.c. The Covid-19 pandemic of 2020 and its aftermath disrupted employment tendencies for each women and men.
working fathers and homemaker moms was effectively established. The labor pressure participation price for males aged 16-64 was 87 p.c, and for ladies, 32 p.c. Because the chart illustrates, the 2 charges moved towards converging over the next seven a long time. By the beginning of 2020, the speed for males had fallen to 69 p.c, however the price for ladies elevated to 58 p.c. The Covid-19 pandemic of 2020 and its aftermath disrupted employment tendencies for each women and men.
Between February and April of 2020 the USA misplaced over 22 million jobs. The primary months of job restoration noticed females returning at a slower tempo than males, however when the chance for distant work turned widespread, it’s credited with fueling a file price of feminine labor pressure participation. A research by the San Francisco Federal Reserve discovered that participation modified for various subsets of the feminine labor pressure: “…girls with out a school diploma disproportionately dropped out of the labor pressure throughout the pandemic, maybe to care for youngsters or sick kin. Nonetheless, we discover that ladies with a school diploma or extra more and more joined the labor pressure throughout this era, doubtlessly due to extra alternatives to earn a living from home.”
Now Return-to-Workplace (RTO) mandates are threatening to erase the positive aspects. Whereas a current survey by McKinsey discovered that 9 out of ten girls need to work remotely all or a part of the time, a worldwide survey discovered that just about two-thirds of CEOs count on staff to return to places of work 5 days per week by 2026.
The enchantment of distant working is shared by female and male employees alike, each part-time and full-time, in keeping with numerous surveys. Companies have contrasting views on the advantages of office-only work: whereas some see increased productiveness when folks earn a living from home, others stress some great benefits of in-person collaboration. Examples abound of employees planning to stop if given an RTO mandate, and of employees keen to just accept much less pay for a distant work alternative. All that is occurring in a demographic atmosphere of fewer births, an ageing inhabitants, and a smaller work pressure.
Return-to-Workplace Mandates
After World Warfare II ended, the nation’s labor pressure returned to civilian life. By the tip of 1945 greater than 4 million troopers returned to civilian standing. Greater than six million girls held wartime jobs in factories and three million volunteered with the Crimson Cross. Authorities archives reporting on girls within the labor pressure throughout World Warfare II reported on the aftermath: “After the warfare, most girls returned house, let go from their jobs. Their jobs, once more, belonged to males. Nonetheless, there have been lasting results. Ladies had confirmed that they may do the job and inside a number of a long time, girls within the workforce turned a typical sight.”
Firstly of 1948 the post-war sample of households with working fathers and homemaker moms was effectively established. The labor pressure participation price for males aged 16-64 was 87 p.c, and for ladies, 32 p.c. Because the chart illustrates, the 2 charges moved towards converging over the next seven a long time. By the beginning of 2020, the speed for males had fallen to 69 p.c, however the price for ladies elevated to 58 p.c. The Covid-19 pandemic of 2020 and its aftermath disrupted employment tendencies for each women and men.
working fathers and homemaker moms was effectively established. The labor pressure participation price for males aged 16-64 was 87 p.c, and for ladies, 32 p.c. Because the chart illustrates, the 2 charges moved towards converging over the next seven a long time. By the beginning of 2020, the speed for males had fallen to 69 p.c, however the price for ladies elevated to 58 p.c. The Covid-19 pandemic of 2020 and its aftermath disrupted employment tendencies for each women and men.
Between February and April of 2020 the USA misplaced over 22 million jobs. The primary months of job restoration noticed females returning at a slower tempo than males, however when the chance for distant work turned widespread, it’s credited with fueling a file price of feminine labor pressure participation. A research by the San Francisco Federal Reserve discovered that participation modified for various subsets of the feminine labor pressure: “…girls with out a school diploma disproportionately dropped out of the labor pressure throughout the pandemic, maybe to care for youngsters or sick kin. Nonetheless, we discover that ladies with a school diploma or extra more and more joined the labor pressure throughout this era, doubtlessly due to extra alternatives to earn a living from home.”
Now Return-to-Workplace (RTO) mandates are threatening to erase the positive aspects. Whereas a current survey by McKinsey discovered that 9 out of ten girls need to work remotely all or a part of the time, a worldwide survey discovered that just about two-thirds of CEOs count on staff to return to places of work 5 days per week by 2026.
The enchantment of distant working is shared by female and male employees alike, each part-time and full-time, in keeping with numerous surveys. Companies have contrasting views on the advantages of office-only work: whereas some see increased productiveness when folks earn a living from home, others stress some great benefits of in-person collaboration. Examples abound of employees planning to stop if given an RTO mandate, and of employees keen to just accept much less pay for a distant work alternative. All that is occurring in a demographic atmosphere of fewer births, an ageing inhabitants, and a smaller work pressure.
Return-to-Workplace Mandates
After World Warfare II ended, the nation’s labor pressure returned to civilian life. By the tip of 1945 greater than 4 million troopers returned to civilian standing. Greater than six million girls held wartime jobs in factories and three million volunteered with the Crimson Cross. Authorities archives reporting on girls within the labor pressure throughout World Warfare II reported on the aftermath: “After the warfare, most girls returned house, let go from their jobs. Their jobs, once more, belonged to males. Nonetheless, there have been lasting results. Ladies had confirmed that they may do the job and inside a number of a long time, girls within the workforce turned a typical sight.”
Firstly of 1948 the post-war sample of households with working fathers and homemaker moms was effectively established. The labor pressure participation price for males aged 16-64 was 87 p.c, and for ladies, 32 p.c. Because the chart illustrates, the 2 charges moved towards converging over the next seven a long time. By the beginning of 2020, the speed for males had fallen to 69 p.c, however the price for ladies elevated to 58 p.c. The Covid-19 pandemic of 2020 and its aftermath disrupted employment tendencies for each women and men.
working fathers and homemaker moms was effectively established. The labor pressure participation price for males aged 16-64 was 87 p.c, and for ladies, 32 p.c. Because the chart illustrates, the 2 charges moved towards converging over the next seven a long time. By the beginning of 2020, the speed for males had fallen to 69 p.c, however the price for ladies elevated to 58 p.c. The Covid-19 pandemic of 2020 and its aftermath disrupted employment tendencies for each women and men.
Between February and April of 2020 the USA misplaced over 22 million jobs. The primary months of job restoration noticed females returning at a slower tempo than males, however when the chance for distant work turned widespread, it’s credited with fueling a file price of feminine labor pressure participation. A research by the San Francisco Federal Reserve discovered that participation modified for various subsets of the feminine labor pressure: “…girls with out a school diploma disproportionately dropped out of the labor pressure throughout the pandemic, maybe to care for youngsters or sick kin. Nonetheless, we discover that ladies with a school diploma or extra more and more joined the labor pressure throughout this era, doubtlessly due to extra alternatives to earn a living from home.”
Now Return-to-Workplace (RTO) mandates are threatening to erase the positive aspects. Whereas a current survey by McKinsey discovered that 9 out of ten girls need to work remotely all or a part of the time, a worldwide survey discovered that just about two-thirds of CEOs count on staff to return to places of work 5 days per week by 2026.
The enchantment of distant working is shared by female and male employees alike, each part-time and full-time, in keeping with numerous surveys. Companies have contrasting views on the advantages of office-only work: whereas some see increased productiveness when folks earn a living from home, others stress some great benefits of in-person collaboration. Examples abound of employees planning to stop if given an RTO mandate, and of employees keen to just accept much less pay for a distant work alternative. All that is occurring in a demographic atmosphere of fewer births, an ageing inhabitants, and a smaller work pressure.